How Do You Take the Subjectivity Out of Evaluating the “Feel” of a Golf Club? Well, this Bridgestone Golf Patent Explains how They do it
They do it with science of course! If you had to guess, which of the following iron and shaft combinations produces a “superior feel”?
a) a forged soft-iron head created from soft iron (S20C), with a steel shaft
b) a forged soft-iron head created from soft iron (S20C), with a graphite shaft
c) a stainless steel iron body having a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) face insert, with a steel shaft
d) a stainless steel iron body having a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) face insert, with a graphite shaft
Also, which combination produces the worst feel? The results may surprise you.
The methodology for evaluating the “feel” of a golf club head is described in a patent that recently issued to Bridgestone Golf as USPN 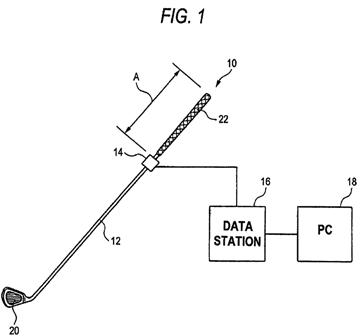
In the apparatus of the present embodiment, when the three-axis accelerometer 14 is attached to the shaft 12 of the golf club 10, there is used, as shown in FIG. 2, a block-shaped jig 28 which is made of an aluminum alloy and which has a recess 24 whose one surface has a circular-arc bottom and a plane 26 opposite the bottom. The jig 28 is fixed to the shaft 12 by use of a single-sided adhesive tape, a double-sided adhesive tape, an adhesive, and the like, while the shaft 12 is inserted into the recess 24 of the jig 28. Further, the three-axis accelerometer 14 is attached to the plane 26 of the jig 28 by use of a single-sided adhesive tape, a double-sided adhesive tape, an adhesive, and the like. In the present embodiment, a distance A between a rear end of the shaft 12 and the three-axis accelerometer 14 is set so as to fall within a range from 250 to 300 mm.
In the apparatus of the present embodiment, the three-axis accelerometer 14 measures vibration of the golf club 10 appearing in a direction X (the axial direction of the shaft), a direction Y (the circumferential direction of the shaft), and a direction Z (a direction from the shaft to the heel) when the golf ball is hit by means of the golf club 10. A measurement signal from the three-axis accelerometer 14 is converted by the data station 16 into the number of vibrations. The vibration appearing in the circumferential direction of the shaft of the golf club 10 measured by the three-axis accelerometer 14 is analyzed by use of the arm-hand vibration measurement filter installed in the PC 28.
In this case, in the apparatus of the present embodiment, vibration of the golf club 10–which is at a specific frequency from 30 to 60 Hz and appears in the circumferential direction of the shaft–is analyzed by means of the hand-arm vibration measurement filter. The feeling of hitting of the golf club 10 is evaluated by means of taking, as an index, a time (time A) from when vibration comes to a specific value falling within a range of 40 to 80% of the peak value until the vibration comes to the peak value; a time (“time B”) from when vibration comes to the peak value until when vibration comes to a specific value falling within the range from 40 to 80% of the peak value; or a total sum of time A and time B.
The feeling of hitting generated by the golf club is evaluated by use of the apparatus shown in FIG. 1. A golf club of iron type is used as the golf club. Specifically, two types of iron heads: namely, an iron head (a soft-iron-forged head) created from soft iron (S20C) by means of forging; and an iron head (titanium face head) a face member formed from a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) fixedly fitted into an opening of a head main body formed from stainless steel (SUS630) whose face is opened, are used as iron heads. Further, two types of shafts; namely, a steel shaft; and a so-called carbon shaft made of a carbon-fiber-reinforced resin, are used. Moreover, four types of golf clubs; namely, a golf club formed by fixing a steel shaft to a soft-iron-forged head (hereinafter abbreviated as “soft-iron-forged/steel”); a golf club formed by fixing a carbon shaft to the soft-iron-forged head (hereinafter abbreviated as “soft-iron-forged/carbon”); a golf club formed by fixing a steel shaft to the titanium face head (hereinafter abbreviated as a “titanium face/steel”); and a golf club formed by fixing a carbon shaft to the titanium face head (hereinafter abbreviated as “titanium face/carbon”), are created.
In the apparatus shown in FIG. 1, a three-axis accelerometer exhibiting sensitivity at a frequency from 0.5 Hz to 2000 Hz is used. The distance A between the rear end of the shaft and the three-axis accelerometer is set to 280 mm. The three-axis accelerometer is affixed to the shaft by means of a double-sided adhesive tape and without use of the previously-described jig. Further, an adhesive tape is coiled around the shaft and the three-axis accelerometer in order to prevent removal of the shaft and the accelerometer in the middle of swinging action. In relation to measurement, the vibration appearing when a golfer actually hits a golf ball by use of the head is measured by use of the three-axis accelerometer. Specifically, the followings are used as devices and software. Three-axis accelerometer: NP-3560B manufactured by Ono Sokki Co., Ltd. Vibration measurement device: Data Station DS2000 Graduo manufactured by Ono Sokki Co., Ltd. Signal conversion-recording software: Throughput disk software DS0250 manufactured by Ono Sokki Co., Ltd. Analysis software: Real-time octave analysis software DS0223 manufactured by Ono Sokki Co., Ltd.
As to analysis, one-third octave band analysis is performed by use of the hand-arm vibration measurement filter. In this case, vibration of the golf club in the circumferential direction of the shaft at a specific frequency of 40 Hz is analyzed by means of the hand-arm vibration measurement filter. As shown in FIG. 3, the feeling of hitting is evaluated by means of taking, as an index, time B from time X when vibration comes to the peak value until time Y when vibration comes to a value corresponding to 75% of the peak value.
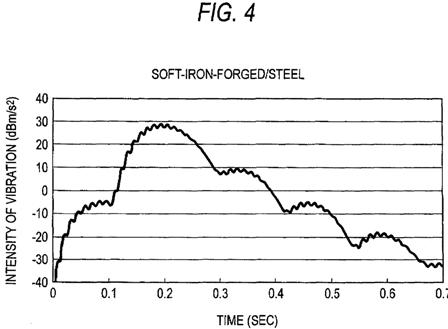
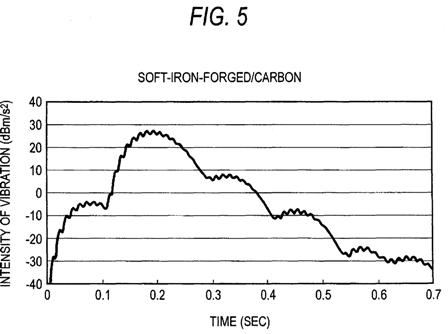
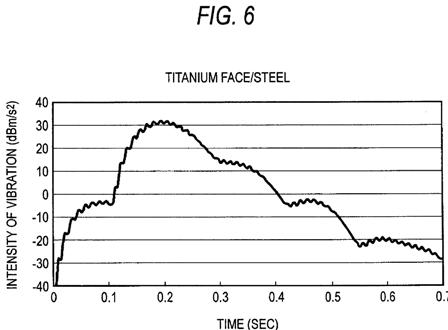
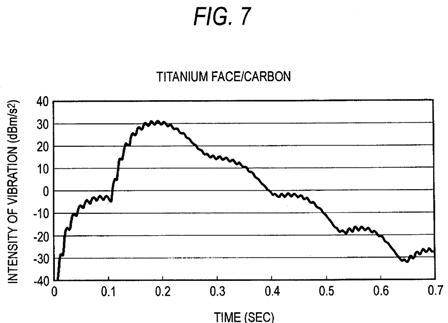
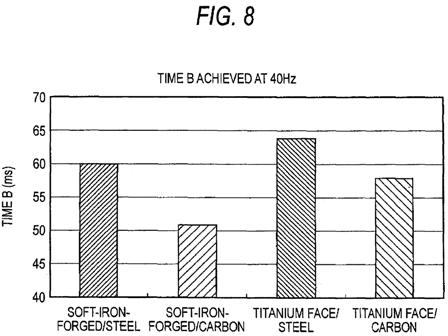
FIGS. 4 through 7 show time-varying changes in the vibration of the golf club appearing in the circumferential direction of the shaft appearing when the golf ball is hit by use of the respective golf clubs. FIG. 4 shows a result of the soft-iron-forged/steel golf club; FIG. 5 shows a result of the soft-iron-forged/carbon golf club; FIG. 6 shows a result of the titanium face/steel golf club; and FIG. 7 shows a result of the titanium face/carbon golf club. FIG. 8 shows results of times B achieved by the respective golf clubs. In the present embodiment, a golf club which yields a longer time B is evaluated as a golf club exhibiting superior feeling of hitting. Consequently, the golf clubs are evaluated in descending sequence of superior feeling of hitting: namely, the titanium face/steel golf club>the soft-iron-forged/steel golf club>the titanium face/carbon golf club>the soft-iron-forged/carbon golf club.
So, did you guess the correct order of the best feeling golf club combination to the worst feeling golf club combination?
a) a stainless steel iron body having a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) face insert, with a steel shaft
b) a forged soft-iron head created from soft iron (S20C), with a steel shaft
c) a stainless steel iron body having a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) face insert, with a graphite shaft
d) a forged soft-iron head created from soft iron (S20C), with a graphite shaft
I am sure that this will make steel shaft manufacturers happy! Does your subjective “feel” agree with the scientific results?
Dave Dawsey – Monitoring Golf Technology
PS – Check out other golf iron invention posts HERE
